15 EKG Others
Pathogenesis


- small depolarization occuring in atrium irregularly, some reach AV and generate QRS, others reach AV during refractory
- result: random QRS

- bottom: normal
- top: AFIB, bumps before QRS but not organized regular bumps. QRS at irregularly irregular (irregular and no pattern to the irregularity)


- bumps are actually T waves, not P
Types and Symptoms



- young pts: healthy AV node, fast

- aortic stenosis: need preload to generate enough output to get past stenosis
- stiff ventricles: need atrial kick to fill the stiff ventricles
- can see cardiogenic shock during Afib

- arrhythmia itself usually not life threatening, thrombus is
- blood flow slower during afib


- when both mitral stenosis and afib, refractory to treatment
- many drugs only test with pts with non-valvular afib

- HR has to be rapid to cause cardiomyopathy
- untreated afib for weeks: EF decline
Risks

- HF: high pressures in RA and RV
- echocardiogram: key test, determine if enlarged heart


- elderly with PNA
- pain after trauma
Treatment


- echo: exclude structural heart disease
- rate control first
- surgery last resort
Rate

- 1st thing to do after pt present with afib and fast HR: decrease HR
- will still have irregular rhythm, but good HR
- pt will feel much better with slower HR
- for elderly, usually all that’s done


- Irregularly irregular static: beta blockers are useful in atrial fibrillation and flutter
- Metronome: beta blockers prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter (“rate control”) (increase AV node refractory period, slow ventricular response rate)

- Illuminated top: non-dihydropyridine CCBs treat supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation with RVR)
- Irregularly irregular signal: non-dihydropyridine CCBs are useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
- Metronome: non-dihydropyridines prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter (“rate control”)

- DJ foxglove: digoxin has antiarrhythmic properties
- Vegas: digoxin exerts direct parasympathomimetic effects via direct stimulation of the vagus nerve -> (more at) AV nodal inhibition
- Irregularly irregular signal: digoxin is useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter) (1st goal is rate not rhythm)
- Metronome: digoxin prevents rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter (“rate control”)

Rhythm

- if still symptoms after slow rate

- synchronized shock, if not can land on T wave = VFIB

- reduced risk of converting back

- Amigo: amiodarone (class III antiarrhythmic)
- “till I die”: -tilide suffix shared by dofetilide and ibutilide (class III antiarrhythmics)
- Soda: sotalol (class III antiarrhythmic)
- Muted bugle: sotalol is also a beta blocker (-lol suffix)
- Heart illuminated on top and bottom: class III antiarrhythmics treat both supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias
- Irregularly irregular signal: class III antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
- Converting the signal: class III antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter

- Class IC antiarrhythmics: propafenone, flecainide
- Flakes: flecainide (class IC antiarrhythmic)
- purple phone: propafenone (class IC antiarrhythmic)
- Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IC antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
- Irregularly irregular signal: class IC antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
- Converting the signal: class IC antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter

- spontaneous back to sinus

- if pt has hypotension/shock with afib: emergent cardioversion
Anticoagulation


- Big GATOR: arGATROban and dabiGATRAN are direct thrombin inhibitors
- Banned foXes: direct factor Xa inhibitors rivaroXaBAN and apiXaBAN
- Directly grabbing foX: factor Xa inhibitors bind directly
- Open mouth: factor Xa inhibitors are oral medications
- Irregularly irregular TV signal: direct Xa inhibitors are used for long term anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation

- Irregularly irregular signal: warfarin is used for long term anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Abnormal heart can increase thrombus formation

- even in sinus rhythm, not completely normal atria, some risk of stroke
- can have short asymptomatic afib


Surgery


- in many cases afib initiated by PA travel to atria
- treat afib by catheters that burn myocyte around PA, create small area of nonconducting scar
AFLUT

- circuit in RA going around and around, each time generate sawtooth pattern, some are conducted to V




- special catheter, burn line of myocyte in atrium, disrupt electrical signal
- much easier than AFIB ablation
AVNRT

- normally: single speed at AV
- AVNRT: dual pathways

- people develop tissues in AV that conduct at different speed
- activity comes from SA, splits into slow and fast pathway
- fast pathway sends signal down AV and also another one back to slow pathway, cancel out with slow pathway
- sinus rhythm: signals cancel out, person asymptomatic

- dual pathway and PAC
- signal down dual pathway at time when fast pathway is refractory (long RF period)
- slow pathway recover quickly
- activity go down slow pathway, once reach bottom, fast pathway recovered, so go back up fast and down from slow
- result: reentrant circuit, tachycardic rhythm

- AV nodal reentry tachycardia
- no p waves: rhythm generated by AV node
- when it comes back up, sends retrograde up to atrium = P wave
- narrow QRS: still using AV
- fast HR

- feel heart pounding
- conduction in slow pathway is already slow, if slow down more = block
- vagal maneuver: hold breath, slow down heart with increased parasympathetic
- adenosine: very flushed and chest discomfort

- recurrent: BB, CCB, slow AV
- if med fail, surgical

- Swing dancing: adenosine (a purine nucleoside with antiarrhythmic properties)
- Purine shaped gate: adenosine is a purine nucleotide
- A1 Swing: adenosine activates inhibitory A1 receptors on the myocardium and at the SA and AV nodes
- Falling calci-yum ice cream: activation of A1 receptors suppresses inward Ca2+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP
- Banana flying out of cup: activation of A1 receptors increases outward K+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP)
- Note shaped dance floor: adenosine inhibits the AV nodes (decreased AV conduction, prolonged AV refractory period)
- Disconnected bottom of heart: adenosine decreases atrioventricular conduction
- Dilated coronary crown: adenosine causes coronary dilation (mediated by A2 receptors)
- Illuminated #1 top of heart: adenosine is a first line agent for acute treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. PSVT)
WPW

- pt: extra piece of tissue (bypass track, white cursor) capable of conducting electricity between atria/ventricles in both directions
- electric current will go down AV node but also through atrium to bypass track = early deflection, delta wave


- P before every QRS, but QRS begins as soon as P ends
- very short PR
- inferior lead deep Q
- portion at different angle
- early activation of ventricle via bypass track

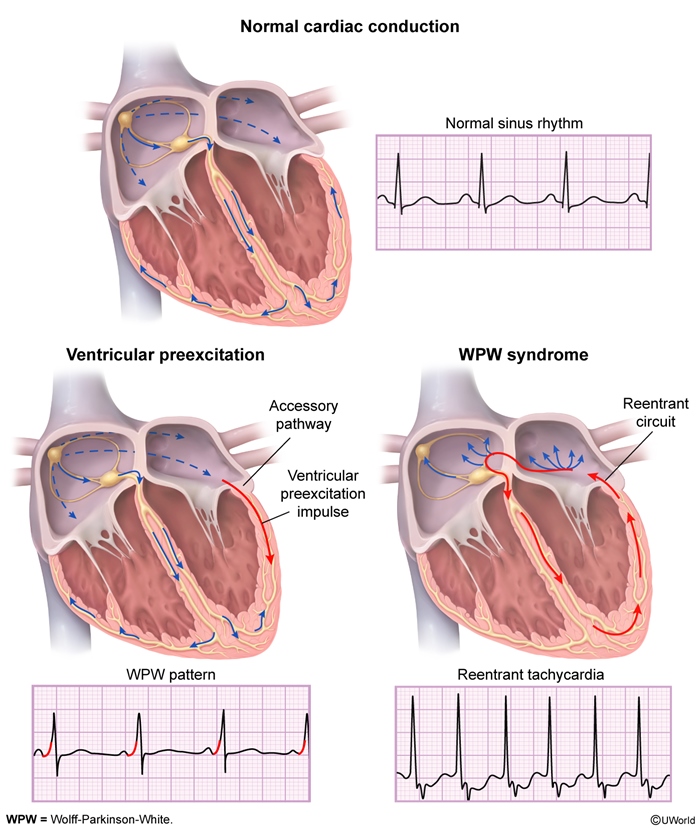
- different from AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia
- ortho: “correct”
- antidromic: go down bypass tract, initiate ventricles abnormally, wide QRS

- pattern: asymptomatic
- syndrome: symptoms

- Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IA antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
- White wolf pack: class IA antiarrhythmics treat Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome (a type of SVT) (extra pathway stopped)

- AFIB, if slow conduction through AV node, more impulse sent through bypass tract
- highly complex management (electric cardioversion or ibutilide/procainamide). Not important
Links to this note


























































