15 Na Disorders
- related: step 1 Renal


- both results lead to brain symptoms
Hyponatremia


Plasma osmolality


- albumin minor contributor, not in equation, more important for oncotic pressure

- 1.6 meq/L decrease in Na for every 100mg/dL increase in glucose


- substances interfere with Na measurement
- triglycerides
- post-TURP


- low osmolality: unknown cause

- Low usine osm: post TURP, beer potomonia
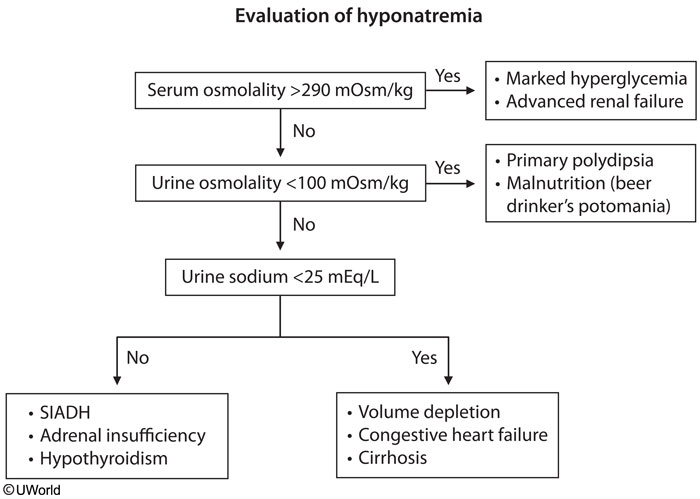

Urinary Sodium

- in reality, no normal levels because varies
- intake equals excretion
- urine Na < 10: extrarenal including CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome
- urine > 20: renal including AKI, CKD
- Patients with SIADH are typically euvolemic; therefore, urine sodium concentration is typically elevated (>40 mEq/L), unlike in patients with hypovolemia.
Urinary Osmolality


- ADH controls above 3 tests



- if body responding appropirately
- urinary Na may vary with dietary intake

Causes


HF

- high Uosm because ADH high
Renal Failure

- renal failure: concentrated urine even at baseline. Can’t excrete water
Diuretics

- hyponatremia common with thiazides

loop diuretic effect:
- decreased Na absorption, increased osm at CD, decreased Na/water absorption
- interstitial high osm eliminated, lower driving force to remove water
- result: very hard to reabsorb water and become hyponatremic
thiazide:
- Na blocked, increased osm at CD, decreased water/Na absorption
- medullary osm intact: continue to maintain ability to absorb free water
- result: excrete Na but absorb water = hyponatremia

ADH and SIADH

- reason why athletes drink Gatorade and not water

- hypothyroidism: high ADH with low thyroid


- no crackles, ankle edema

- stroke, brain bleeds, tumor
- any kind of pulmonary diseases, small cell lung cancer

- Inappropriately wet head: cyclophosphamide can cause hyponatremia due to SIADH

- clinical euvolemia: absence of signs


Psychogenic

Diets

- common theme: little Na ingestion
- kidney must maintain minimum osm

- pt on restricted diet can only excrete 10 water


Summary
Volume and Osm

- hypervolemic: physical exam signs. Use loop diuretics and not thiazide

- Mostly hormone derangements
- low Uosm: kidney response normal

- measure UNa to differentiate
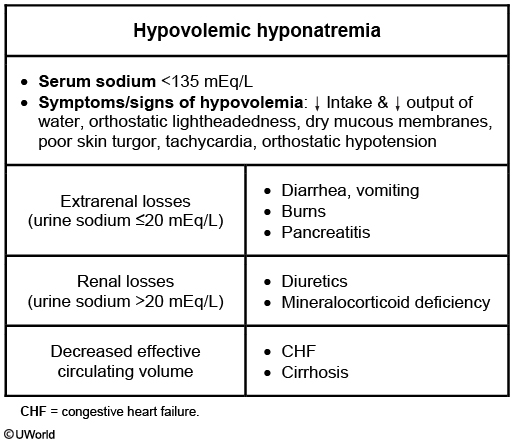
- hypovolemic: Low sodium, low water, but a lot less Na
- diuretics, adrenal insufficiency (acidosis, hyperkalemia), GI loss, 3rd spacing (pancreatitis)
- Treat with NS
ADH and Osm

- red


Treatment


- acute hyponatremia: correct as fast as can (e.g. surgery causes low Na)
- chronic hyponatremia: correct slow
- high risk: alcoholics, liver disease, malnutritioned, hypokalemia
- 10 meq correction 1st day
Hypernatremia



DI


- hypernatremia happen in central lesion



- won’t raise bp

- thiazide, endomethacin (NSAID), amiloride
Treatment
- calculate free water deficit